What is Insulation R-Value?
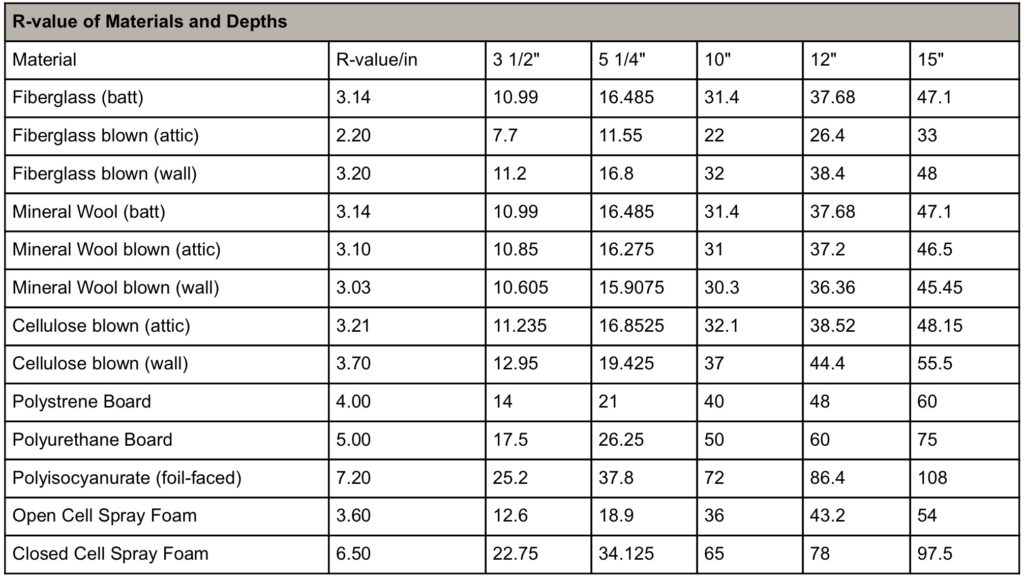
The short, sweet and technical way of putting it, Insulation R-Value is a measure of resistance to heat flow through any given material. In theory, the higher the value, the greater the resistance. Think of it like little tiny football players blocking the heat from coming through. Only, they can’t stop it completely, just keep as much as possible from getting through.
Now let’s get into the long explanation, and we’ll try to make it a one stop shop regarding this subject. The Insulation R-Value or thermal resistance is how the insulating material’s resistance to heat flow is measure. The value depends on the kind of insulation, thickness, and density. By adding more layers to your home insulation, you increase the R-value and the resistance to heat flow. You can contact your local insulation contractor to help you figure out how much insulation your home needs. You can use this link in our website to use a reference guide for the state of Texas if you are located within it, we also provided links to other guides if you are looking into other regions within the United States.
The more you know…
There are numerous guides and sources as to the recommended amount of Total R-Values, but you don’t have to look further than our very own U.S. Department of Energy. Below is a snip of the guide, to see more in depth review of the topic visit them at energy.gov
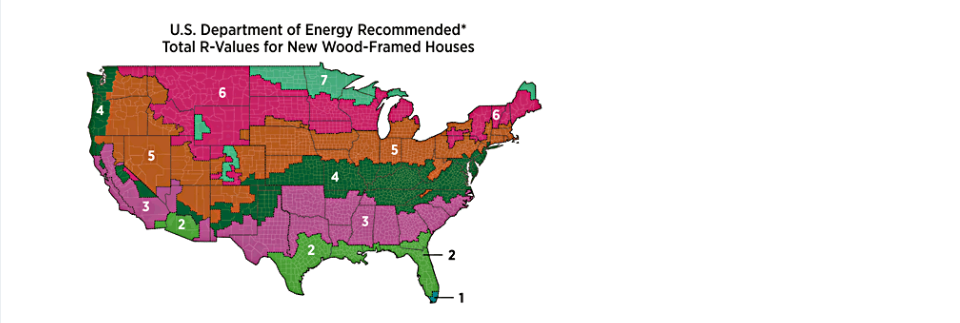
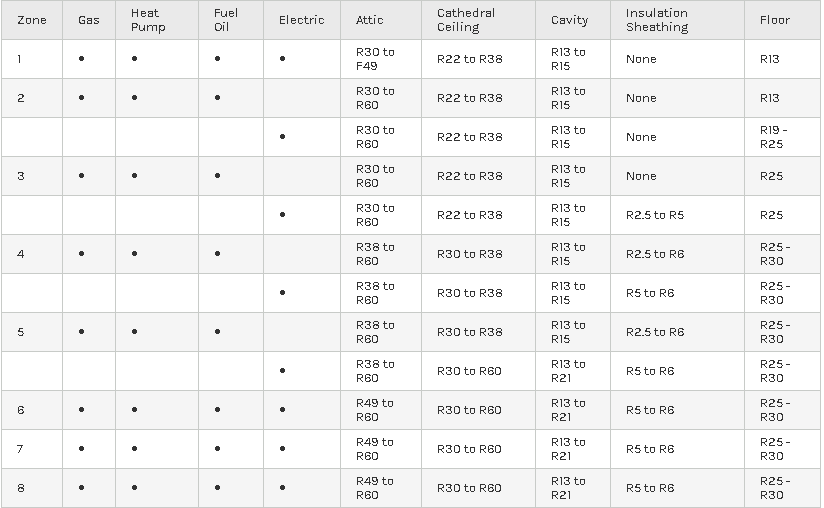
The energy.gov website suggests that “The effectiveness of an insulation material’s resistance to heat flow also depends on how and where the insulation is installed. For example, insulation that is compressed will not provide its full rated R-value. The R-value of a wall or ceiling will be somewhat different from the R-value of the insulation itself because heat flows more readily through studs, joists, and other building materials, a phenomenon known as thermal bridging. In addition, insulation that fills building cavities densely enough to reduce airflow can also reduce convective heat loss.